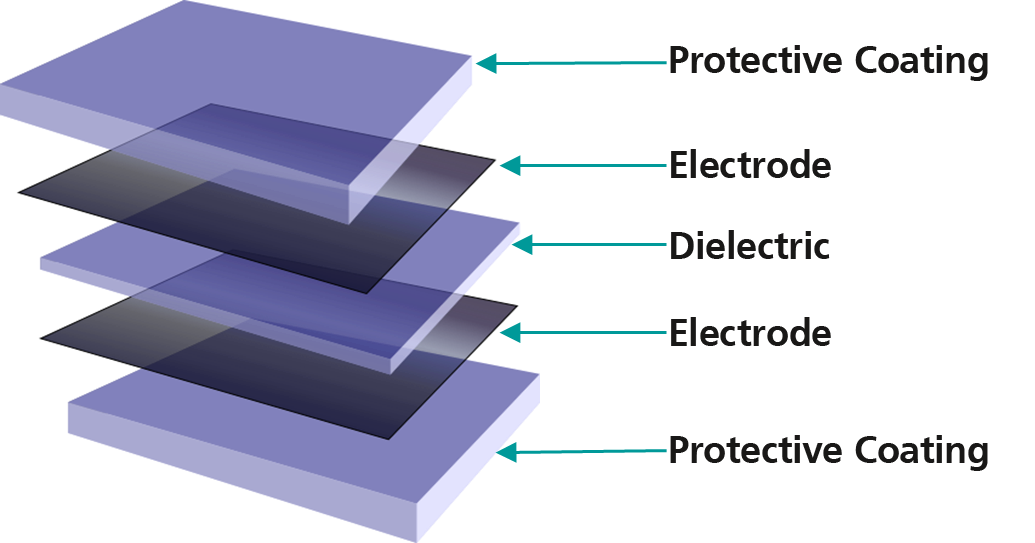
Dielectric elastomers belong to the family of electroactive polymers (EAP) and form flat multilayer systems. They consist of an electrically non-conductive elastomer film with conductive, stretchable electrode layers on both sides. From an electrical engineering perspective, it is a flexible, stretchable plate capacitor with outstanding material properties. Dielectric elastomers can be used for a wide variety of technologies such as mechanical sensors, actuators, and generators.
Advantages and material adaptation
The dielectric between the electrodes can consist of various elastomers. Silicone elastomers are particularly advantageous because they:
- Are chemically inert
- Can be used in a wide temperature range (-50 to +200 °C)
- Offer high mechanical variability
- Can be processed into thin layers
Fillers can be used specifically to adjust the dielectric constant and reduce the layer thickness in capacitive applications. In addition, the electrodes can be applied in almost any geometry using screen printing.
This flexibility makes dielectric elastomers ideal for applications in sensors, actuators, and energy conversion.